Leveraging data mining for smarter business decisions: Why businesses need data mining more than ever?
Whether data is the new oil is a debate for another time, yet its importance in this economy can’t be denied. In a global world where digitisation has made the possibility of a massive data explosion and breadcrumbs a reality, data analysis, or the lack of it, is what changes the future course of businesses. While there has been quite some buzz around data mining services and their significance for businesses, small and large alike, we have compiled everything you need to know about data mining and why it is indispensable for business growth. Let’s begin!
So, what is data mining?

Like traditional mining, where valuable minerals and metals are extracted from the earth’s crust, data mining involves extracting valuable and relevant information from heaps of data. It is an automated or semi-automated technical process that includes analysing large chunks of scattered data. Data mining treats data as a vital commodity that takes a business ahead in all spheres of operations, ranging from research to marketing and even policy-making. It is also known as knowledge discovery in data or KDD.
Data is being generated every day with new connected devices. Now, we have social media, GPS sensors, phones, smart air conditioning systems, connected refrigerators, Wi-Fi, fitness trackers, and smart assistants generating more and more data as we speak. Data, which was earlier a sparse commodity, a rare asset, is now no longer a siloed and inaccessible entity. It is free-flowing and easily available. However, the one thing that has remained unchanged is its utilization. Every business wants to bank on data to refine its processes, transform customer interactions, and improve its products, but the key to unlocking its potential remains elusive.
This is where data mining services come into the picture. Simply put, data mining takes the complexity out of data management and helps businesses uncover patterns, anomalies, irregularities, and relationships between disparate data sets. Since minimal human intervention is involved, data mining solutions help businesses cut down on extra costs and avoid drowning in the complexities of data management.
Data mining uses machine learning algorithms and statistical analysis to turn data into knowledge, including defining the target sets and predicting the outcomes.
Also read: Understanding Data Mining With the Help Of Case Studies On Data Mining In Market Analysis
What is a data mining application?
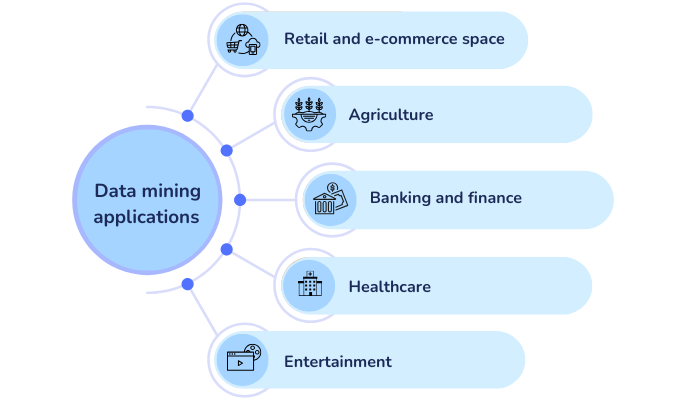
Data mining applications are not just theoretical concepts but practical tools industries use daily. These are specific use cases where data mining techniques are deployed to extract relevant information and actionable insights, leading to optimal productivity and desired outcomes.
Trend detection, sales forecasting and sentiment analysis in Retail and e-commerce space: Businesses are using data mining to establish patterns between sales, purchasing history and consumption behaviours. They can detect offers resonating with their customers and gain insight into their purchasing power and buying patterns, resulting in more sales. Case in point: the controversial Target pregnancy predictive analysis.
Data mining applications in retail are based on recency, frequency, and monetary grouping, commonly known as RFM. Based on this grouping, the marketing team customises product recommendations, upselling and cross-selling campaigns, and promotional plans for each set.
In e-commerce, data mining applications are even more lively and unmissable. The ‘frequently bought together’ and ‘People who viewed this product also bought’ or ‘You might like this’ is nothing but data mining at play in its full glory that profiled customers into segmentation and analysed their purchase history to identify patterns further. For instance, customers who have purchased water filters may purchase the filters again, or customers purchasing baby food may want to buy baby food.
Predictive analytics in Agriculture: Data mining in agriculture has been a game-changer. In countries like India, where agriculture is a major contributor to the economy, descriptive and predictive data mining has enabled pre-harvest forecasting for farmers, researchers, agricultural scientists, and the government. They can utilise the data to make timely decisions regarding pricing, storage distribution, climatic conditions, crop rotation planning, and import-export.
Predictive analytics, compliance checks and entity mapping in Banking and finance: Data mining has proved to be a blessing for financial institutions. According to a World Bank Report, banks recorded a historic reduction in bad debts using data mining techniques. Similarly, banks and financial institutions can curb financial fraud in real-time, which results in losses of around $33 billion and is on the rise every year using data mining techniques such as anomaly detection.
Banks are also employing data mining tools preemptively to detect patterns of illicit and money laundering activities to ensure AML compliance and prevent financial fraud. Investment banking also relies on data mining techniques for investment insights and increased profitability. Goldman Sachs uses machine learning and AI tools to forecast and capture bullish or bearish sentiments. The investment firm has leveraged predictive analytics to determine profitability and target undervalued shares.
Research data cataloguing in Healthcare: In healthcare, data mining services have been beneficial in creating disease prediction models, evaluating risks and enabling clinical decision-making from large, unstructured data sets, which are public healthcare databases. This has facilitated preemptive healthcare and effective treatment programs for patients.
Predictive analysis in Entertainment: Online streaming platforms like Netflix and Amazon use predictive analytics to create customised content and provide a better user experience by developing content that is suitable and liked by their audience. These insights also inform content delivery based on devices and network conditions, with many platforms using an M3U8 player for adaptive streaming and smooth playback. The movie industry worldwide also uses data mining services to forecast box office success, budget strategy, and release time.
Data mining methods are used to unearth the most crucial data across the industry to improve and enhance organisational decision-making. With the advancements in AI and Machine Learning algorithms, data mining tools are now more sophisticated than ever and ready to handle large sets of data quickly than ever.
Difference between data analytics and data mining
Data analytics and data mining are often used interchangeably. Data mining is an integral part of data analytics, a small yet vital aspect of the data ecosystem.
Data mining involves discovering patterns and anomalies in large sets of data using data mining tools, whereas data analytics is the process of interpreting data to generate meaningful insights within data. It is not the difference in the tools or approach. It is the intended end result that determines whether you want to analyse the data or establish a pattern within the dataset.
What are data mining tools?
Various types of software are available in the market designed to accelerate and execute data mining techniques. These are referred to as data mining tools and are supported by cutting-edge machine learning and AI capabilities, making data mining easier than ever. The latter has allowed the automation of data mining techniques and has addressed the challenges of scalability and speed faced by businesses handling large volumes of data, leading to greater adoption across industries.
What does the data mining process entail?
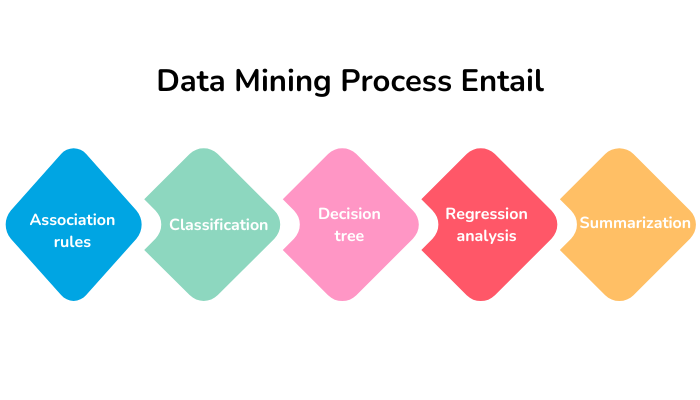
While the data mining process may vary depending on datasets and pain points, these are the stages it usually follows.
- Association rules: It is a machine learning technique based on the if / then rule-based method and is used for market basket analysis. It helps establish relationships between different yet related products, facilitates businesses’ framing of cross-selling strategies, and develops an understanding of customers’ purchasing behaviour.
- Classification: It involves classifying the existing data in common predefined themes that are already known about them, such as age, location and purchasing history, to plan their marketing promotion better. Clustering, however, is attributed to creating similar data points in clusters without predefined labels. The real-world data mining application example of clustering would be anomaly detection and market segmentation.
- Decision tree: This tree-like visualisation helps businesses compare available options and determine the optimal course of action with the intended consequence.
- Regression analysis: Regression analysis establishes a correlation between different variable inputs. A real-world application example of this would be companies building inventory stock ahead of a season rush.
- Summarization: This stage involves a brief report of issues, objectives, and findings supported by visualisation.
Data Mining Benefits
Data mining offers several benefits to small and large businesses across industries. Some of them are:
Discovering insights and trends: Data mining helps businesses dive deeper into data and find trends, correlations, and anomalies in disparate and large datasets. This knowledge empowers business think tanks to make informed decisions and prepare for the future. Whether it is stock inventory, customer relationships, policy-making, or competitive advantage- data mining transforms raw data into knowledge, rightfully earning it the name KDD or Knowledge Discovery in Database.
Reduction in unpredictable expenses: Data mining techniques enable businesses to identify loopholes and bridge gaps between customer communication, supply chain, and logistics, leading to operational efficiency and optimised workforce productivity.
Data efficiency: Data mining processes can handle disparate and structured data sets originating from different sources at any point within an organization, offering a holistic and complete picture of data and enabling businesses to make informed decisions.
Enhancing physical security systems: Data mining techniques can also be applied to physical security systems to analyze data from sources like video surveillance, access control and sensor networks. Solutions such as Avigilon Alta Protect utilize advanced analytics to detect unusual patterns, predict potential threats and trigger real-time alerts, ultimately creating safer environments for businesses.
Opportunities, Challenges and Blind Spots

Data has touched every aspect of our existence. It has impacted businesses, societies, communities, governments, and industries. It has changed our entertainment and education. It has changed our shopping patterns, lifestyles, and how customers engage with businesses. As data becomes too overwhelming to handle across virtual landscapes, it becomes more challenging to contain and make sense of.
According to an IDC report, “Data Age 2025,” the world will reach 175 zettabytes of data by 2025. Furthermore, a single user will interact with their connected devices around 4,800 times per day by 2025, which is an interaction per 18 seconds!
Not sure what this wealth of data means? Let’s put this into perspective.
- It is 40 trillion years of movie streaming.
- We need at least 1.5 trillion iPhones to store this data.
- The number of DVDs needed to store this data could circle Earth 222 times.
- It might take 1.8 billion years to download this data and 81 days if we enroll everyone on this planet to do this.
Crazy, right? It is challenging. With such massive data comes the usual problem, as massive as the opportunities they bring forward. While it is one thing to try to understand it and use it to chart future plans, there are troublemakers in the segment, too. These are companies trying to lap up customers’ data without their consent and giving access to their employees who have no business accessing it. This results in data breaches and reputational damage- making data management all the more difficult. When businesses don’t know what they need, they have copious amounts of data that they don’t know what they need, resulting in a burdened system and employees.
While bringing out relevant and actionable insights and handling large volumes of data, data mining grapples with an abundance of irrelevant data and a lack of expertise. Data mining requires coding experience and knowledge of data mining languages such as Python, R and SQL- causing a dent in the Human Resource budget of businesses that can’t afford to hire a team. Besides, in-house capabilities are rarely capable of handling large volumes of data, leading to incorrect and misleading approaches and causing more harm than benefits. It can also embroil businesses in uncertainty, especially when the data mining results aren’t up to their expectations, failing to understand that it could be incorrect data or the modelling approach. If the data includes private and sensitive information, such as in healthcare, it is a PR disaster waiting to happen. It can also cause regulatory compliance and cybersecurity issues for the businesses if ignored.
Additionally, creating a new data pipeline from the ground up or buying data from external sources can be quite expensive for businesses that lack the necessary expertise. Data dredging is more common than we see, making correlations and revealing patterns when there are none.
While data mining techniques are highly automated, human intervention is indispensable. This is where BizProspex comes in. We are a data mining services provider with an expert team of data engineers, data architects, and researchers to ensure that your business gets data mining right and brings maximum value for money. Drive business growth, value, and innovation with data mining services that are tailor-made for your business and right for your budget. Don’t let your business get caught up in the complexities of data mining and run into unpredictable expenses. Trust the expert! Trust one of the leading data mining services providers available 24/7 and helps you define data from noise.
Want more information on BizProspex data mining solutions? Contact us here or send us an email to [email protected]

